什么是加密货币?
加密货币是利用密码学原理来保障交易安全、控制新货币的生成及验证资产的转移的一种数字货币。与传统货币不同,加密货币通常并不依赖于中央银行或政府机构的支持和监管,而是基于去中心化的区块链技术。区块链是一种分布式账本技术(DLT),它记录所有的交易,通过全网共识来验证每一个交易的合法性。
第一种加密货币比特币于2009年被创造出来,随后以太坊、瑞波币等其他加密货币相继涌现。加密货币的引入不仅引发了金融交易方式的革命,也推动了技术的发展,其背后的区块链技术在多个领域中显示出巨大的应用潜力。
加密货币的工作原理
加密货币的基础是区块链技术。区块链由一系列连接的区块组成,每个区块中包含了一定数量的交易记录。当用户进行一项交易时,会通过加密算法生成一个交易请求,这个请求会被广播到整个网络。网络中的“矿工”节点会竞争去解决一个复杂的数学问题,并将交易打包到一个新的区块中。成功的矿工将获得新生成的加密货币以及该区块内交易的交易费用作为奖励。
经过网络中的节点达成共识后,该区块会被添加到现有的区块链上,交易也随之被确认并记录在账本上。这个过程确保了交易的不可篡改性和透明性,使得每一笔交易都可以被追踪,而无须依赖信任的中介机构。
加密货币的优势与挑战
加密货币为金融系统带来了诸多优势。例如,它们能够在全球范围内实现快速且低成本的转账,减少了传统银行业务中的中介费用。同时,加密货币的去中心化特性保护了用户的隐私,从而增强了用户对资金的控制权。
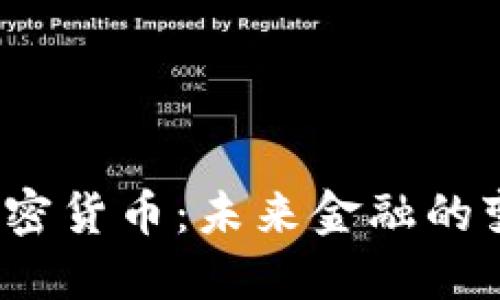
然而,加密货币的兴起也面临诸多挑战。例如,许多国家对加密货币的监管尚不明确,自然导致了投资风险的增加。此外,网络安全问题也是一个重大风险,加密货币交易所常常成为黑客的攻击目标,导致用户资金被盗。
Investing in cryptocurrency: Risks and rewards

Investing in cryptocurrency can be both rewarding and risky. On the one hand, early investors in Bitcoin and Ethereum have seen massive returns on their investments, as the prices of these digital assets have skyrocketed. On the other hand, the notorious volatility of cryptocurrency markets can result in significant losses in a short amount of time.
Investors interested in entering the cryptocurrency space should first conduct thorough research and understand the specific cryptocurrency they plan to invest in. It's crucial to consider factors such as market capitalization, technology behind the cryptocurrency, team credibility, and future use cases. Long-term holding might be beneficial for discerning investors, while others might opt for day trading to benefit from quick price movements.
How is cryptocurrency regulated?
The regulatory landscape for cryptocurrency varies significantly between countries and regions. While some jurisdictions, like Malta and Switzerland, have embraced cryptocurrencies, providing a clear regulatory framework, others have taken a more cautious approach, imposing strict regulations or outright bans.
The goal of regulation is to ensure consumer protection, prevent fraud, and reduce the risk of money laundering and terrorist financing. Countries may require cryptocurrency exchanges to register and comply with Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) laws. As the industry continues to evolve, regulatory bodies strive to balance innovation with security, creating a more stable environment for cryptocurrency transactions.
What are real-world applications of blockchain technology?
Blockchain technology, which underpins cryptocurrencies, offers a wide range of applications beyond digital currencies. Its decentralized nature and transparency make it suitable for various sectors. In supply chain management, blockchain can enhance traceability by allowing stakeholders to track products from their origin to the consumer. This can greatly reduce fraud and increase accountability.
In healthcare, blockchain can securely store and share patient records across different healthcare providers, ensuring privacy and security while improving patient care. Additionally, the technology is being explored for voting systems, intellectual property rights management, and even digital identity verification.
Future of cryptocurrency and blockchain technology
The future of cryptocurrency and blockchain technology looks promising, given the growing interest from institutional investors, corporations, and governments. Central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) are being developed by numerous countries, aiming to blend the benefits of digital currencies with the stability of traditional fiat currencies.
Moreover, the integration of blockchain in various industries is expected to expand, leading to increased efficiencies and reduced costs. As technology matures, it may lead to more robust regulatory frameworks that encourage innovation and protect consumers, creating a healthier environment for cryptocurrency growth.
### 可能相关问题 1. **加密货币的投资风险有哪些?** 2. **区块链技术的应用领域有哪几种?** 3. **国家对于加密货币的监管政策如何?** 4. **如何选择适合自己的加密货币投资?** 5. **未来加密货币的发展趋势是什么?**